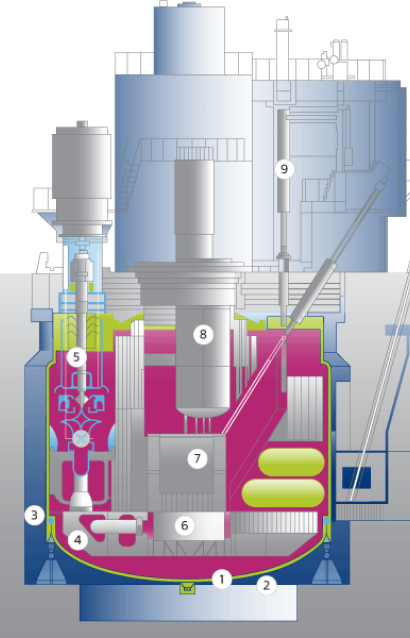
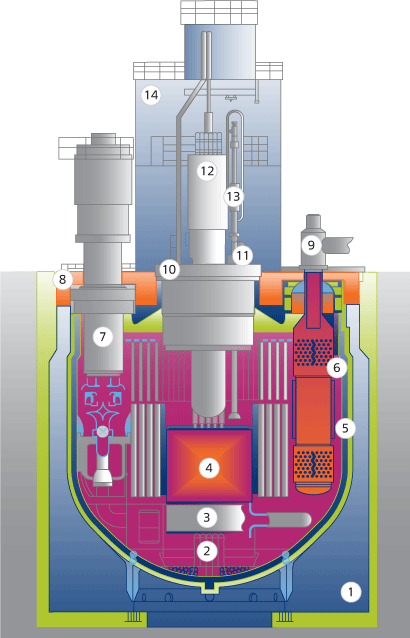
The power units are made on the base of the three-circuit scheme. Liquid sodium circulating along the first and second circuits is used as the heat transfer medium. The BN is housed in a sealed protective containment preventing from any external effects or radionuclide release into the environment in case of a hypothetical accident.
Highly-enriched uranium dioxide and mixed uranium-plutonium fuel are used for the BN.
The reactor employs an integral concept where all equipment of the primary circuit is placed inside the reactor vessel. The reactor accommodates three main circulation pumps, six intermediate heat exchangers “primary circuit sodium – secondary circuit sodium”, as well as the reactor control and protection system and the refueling system.
Sodium is circulating in the reactor along three loops where each loop may run independently of the others. In order to enhance the safety, the reactor is placed into a special guard vessel filled with inert gas.
The secondary (intermediate) circuit consists of three loops each of which contains the main circulation pump of the secondary circuit, two heat exchangers “primary circuit sodium – secondary circuit sodium”, one modular once-through steam generator, and an expansion tank. In the tertiary (steam-water) circuit, steam from three steam generators is collected in a common manifold and supplied to the turbine (BN-800 has one turbine and BN-600 has three turbines).
The heat transfer medium of the primary circuit is heated up while passing through the reactor core and is delivered by three parallel circulation loops to six intermediate heat exchangers where it transfers heat to the heat transfer medium of the secondary circuit and returns to the reactor core. Sodium is pumped through the loops using the primary main circulation pump.