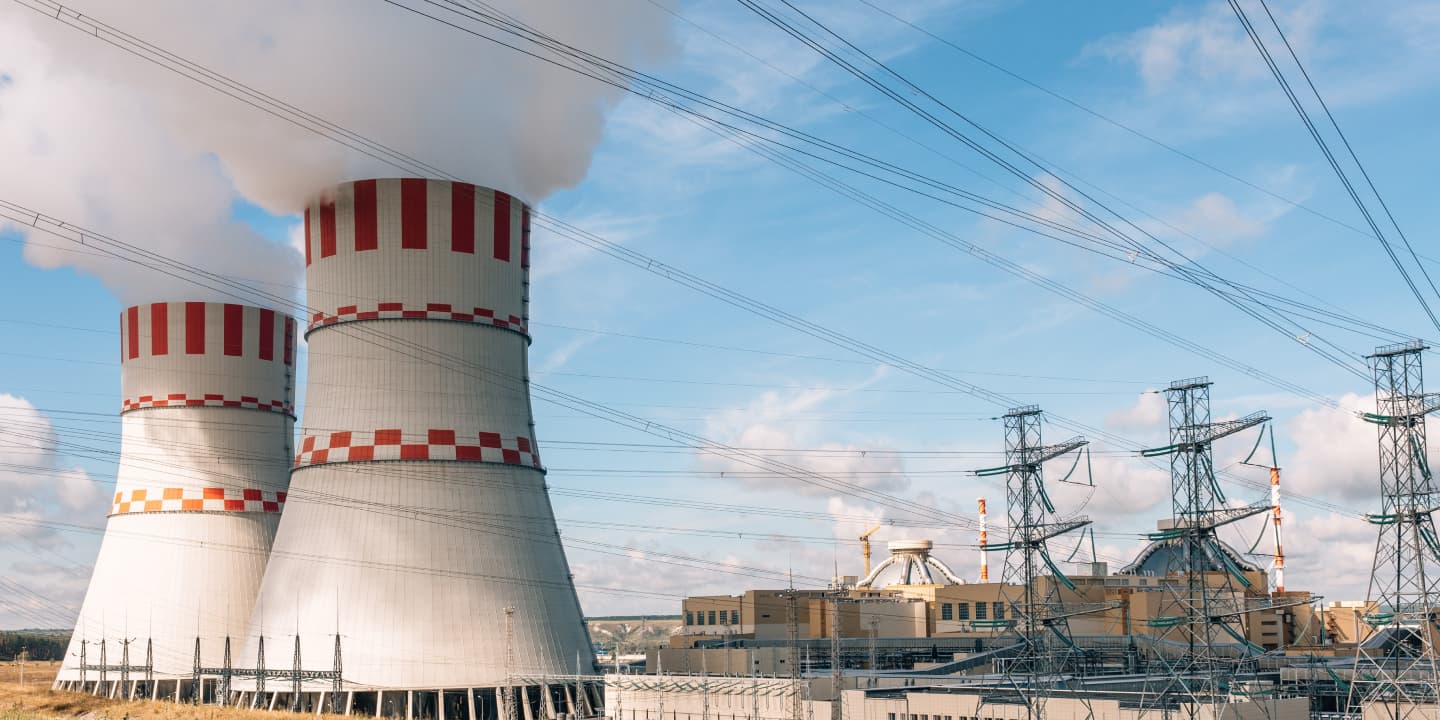
Novovoronezh NPP was constructed in three stages: stage one – power units No. 1 (VVER-210 in 1964) and No. 2 (VVER-365 in 1969), stage two – power units No. 3 and No. 4 (VVER-440 in 1971 and in 1972), stage three – power unit No. 5 (VVER-1000 in 1980).
A new generation 3+ power unit No. 6 with a VVER-1200 reactor unit was commissioned on February 27, 2017. Power unit No. 7 was commissioned on October 31, 2019.
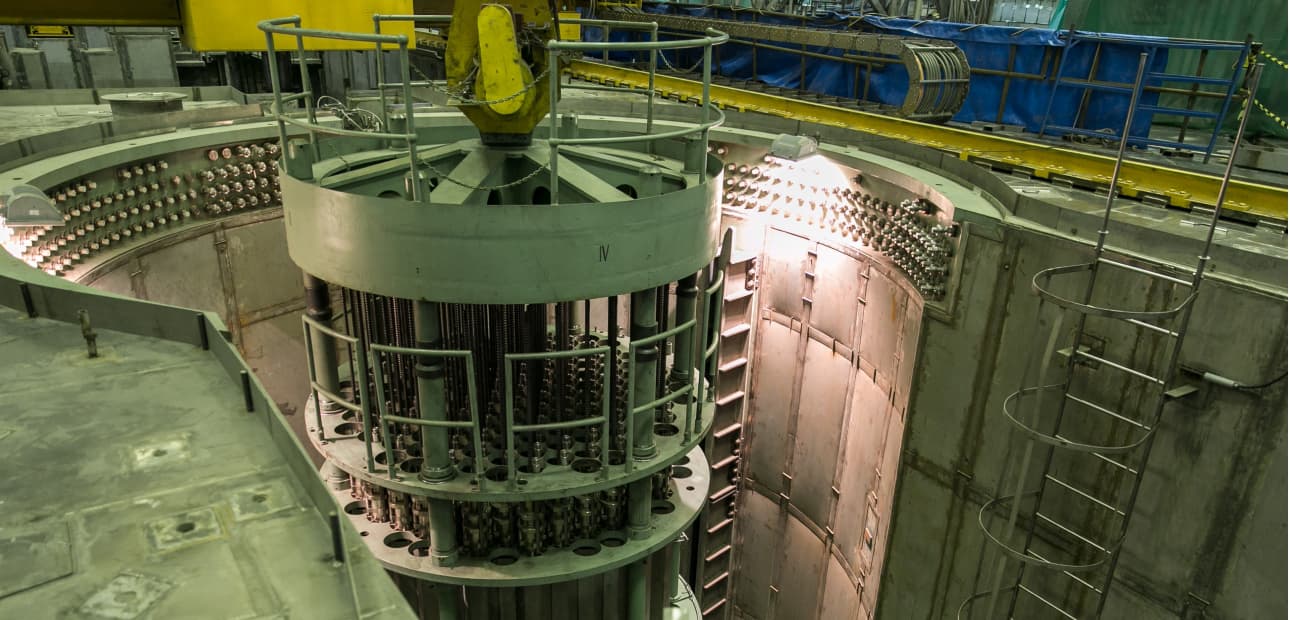
VVER is a shell-type water-cooled water-moderated power reactor. Water, whose boric acid which concentration varies during operation, is the coolant and the neutron moderator of this reactor. Low enriched uranium dioxide is used as fuel in the reactor core. The VVER is housed in a sealed protective containment structure preventing any external effects or radionuclide release into the environment in case of a hypothetical accident.
The process flow scheme of Novovoronezh NPP power units comprises two circuits.
The primary circuit is radioactive. It consists of the reactor, the main circulation pumps, the steam generators, and the pressurizer. The primary circuit is intended for heat removal from the reactor and transfer to water in the secondary circuit. The coolant in the primary circuit is high-purity water under pressure with boric acid dissolved in it, which is a strong neutron absorber.
Water is pumped by the main circulation pumps through the reactor core, where it is heated up to 290-320 degrees for the VVER-1000 and 295-325 for the VVER-1200 due to heat generated as a result of the nuclear reaction. Water in the primary circuit transfers heat to water in the secondary circuit through metal walls of the heat-exchange tubes in the steam generator and returns to the reactor.
The two-circuit system helps to prevent an escape of radioactive elements beyond the boundaries of the primary circuit. The design features six circulation loops at power unit No. 4 of Novovoronezh NPP and four circulation loops at power units No. 5, No. 6, and No. 7.